Simple Easy Basic Sagews Examples With Inputs
Sage Worksheets¶
- Introduction
- What's a Sage Worksheet?
- How to Revert/Undo Changes in a Sage Worksheet
- TimeTravel
- Backups (snapshots)
- Understanding Error Messages
- Help for Programmers
- Extended Documentation
- Concise Documentation
- Source Code
- Tab Completion
- Sage Worksheet Slow When Plotting? Disable svg.
- How Long are Definitions Stored in a Sage Worksheet?
- Wiki resources
- Sage Worksheets
- Conversion utilities
- Help about SageMath
- Howto
- Attach Sage files to Sage Worksheets
- How can I connect an HTML form with my Python code?
- How can I play sounds?
Introduction¶
Sage Worksheets were developed for collaborative, notebook-style computing with SageMath on the CoCalc platform. Like Jupyter Notebooks, Sage Worksheets support many programming environments. More than one language environment can be used in the same Sage Worksheet.
Note: in the CoCalc User Manual, we will generally use the term SageMath to refer to the open source mathematical system that runs on CoCalc and in many other environments. Elsewhere, you may see it referred to simply as Sage.
In CoCalc, there are at least three ways to run SageMath:
- in a Sage Worksheet
- in a Jupyter Notebook
- from the command line in a terminal
What's a Sage Worksheet?¶
A Sage Worksheet is a file ending in .sagews and is subdivided into cells. Each cell has an input region and an output region, which might be 0, 1, 2, or many lines long.
The input can be mathematical, in the Sage syntax, or it could be in many other formats, including Markdown, HTML, Python 2 or 3, and R. To use a format other than Sage syntax, start the cell with a mode directive such ss "%md" for markdown. See this CoCalc blog article for more information about built-in and custom sagews modes.
When you run a cell, by clicking Run or typing Shift-Enter , the input is executed (or formatted, for text processing). The result appears in the output after the calculation is done.
To begin work on a Sage Worksheet, create a file ending with .sagews .
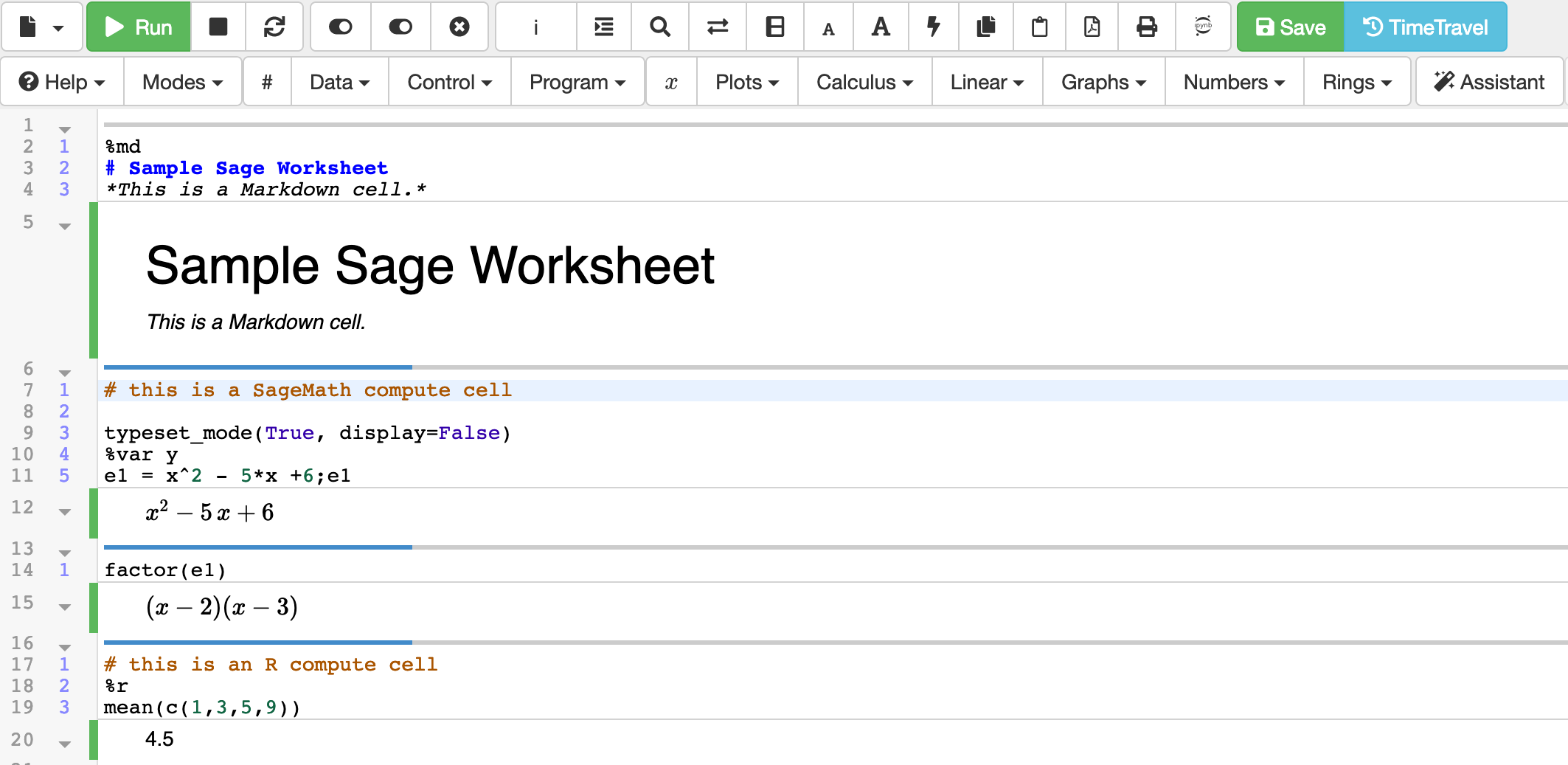
example of a Sage Worksheet
How to Revert/Undo Changes in a Sage Worksheet¶
For tiny changes, control+Z (or command+Z on a mac) will give you an instantaneous undo.
When it comes to undoing larger changes, one of the most useful things about CoCalc is that it will keep all versions of all of your files. This means that you can revert back to previous versions easily.
TimeTravel¶
From any worksheet, click on TimeTravel.
Using the slider, look at all the versions. Find the revision that you want and then click "Revert live version to this."
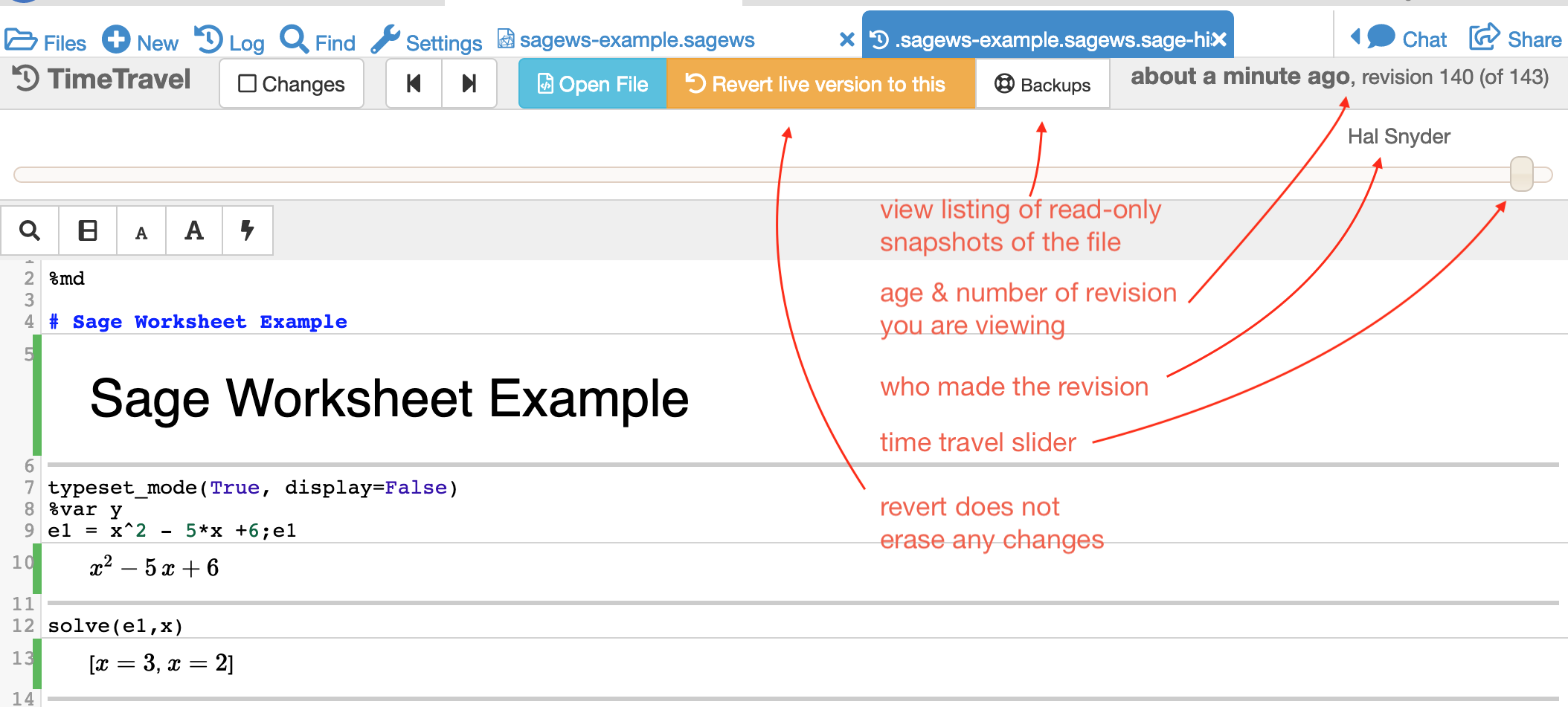
looking at a Sage Worksheet with TimeTravel
Backups (snapshots)¶
For a list of snapshots taken by CoCalc, use the Backups button from the TimeTravel view or the Files list. Note that these backups are read-only. If you want to continue working on a file from a snapshot in Backups, you will need to copy it into a writable folder in your project.
Understanding Error Messages¶
Question: I did xyz and now I have this huge error message! Why?
Often when SageMath encounters an error, a long error message appears. This output is called a "stack trace" and it can be very useful to experienced programmers. However, often it is enough to look at the last line of the error message to understand what has gone wrong.
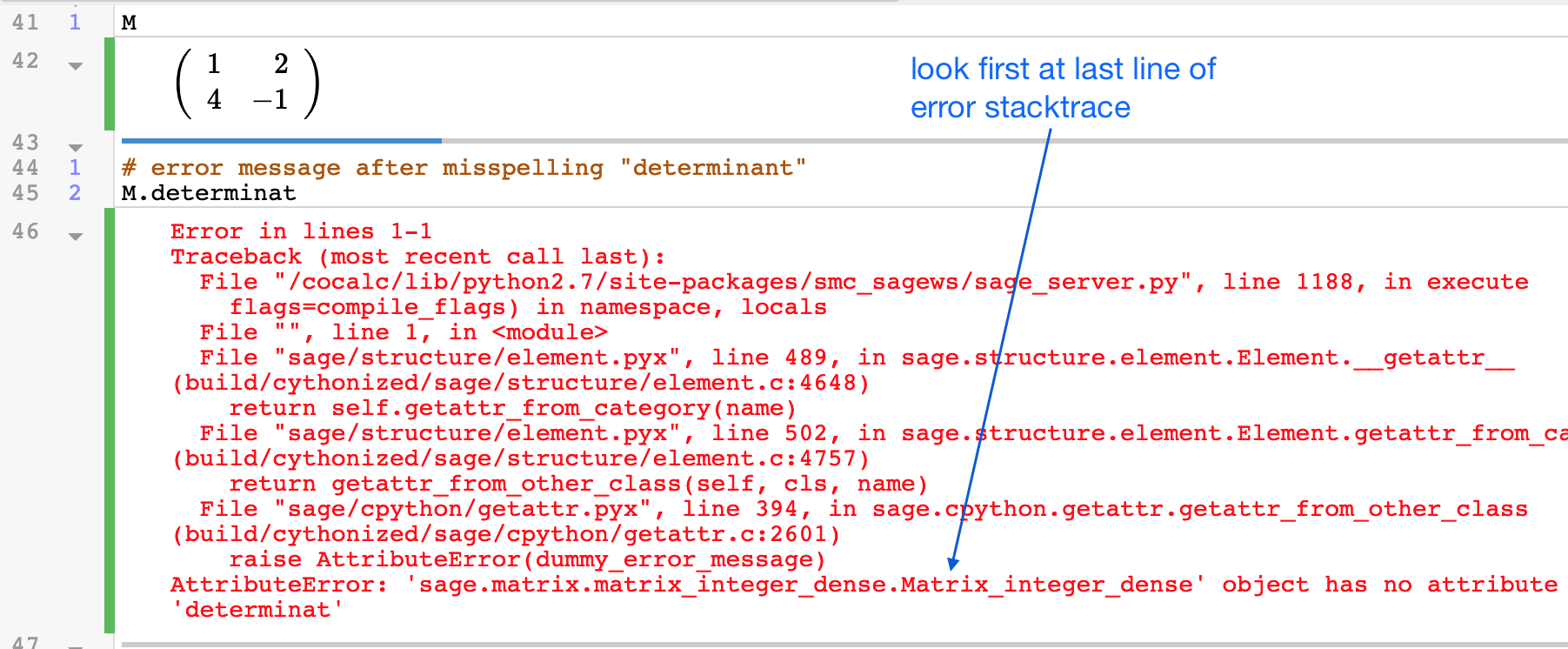
making sense of error messages
Help for Programmers¶
Extended Documentation¶
To see verbose documentation for language features, including commands, methods, and attributes, use the help() function.

Concise Documentation¶
To see concise documentation (docstrings) for language features, attributes, append a single question mark and run the cell. This information is similar to what you get with help() .
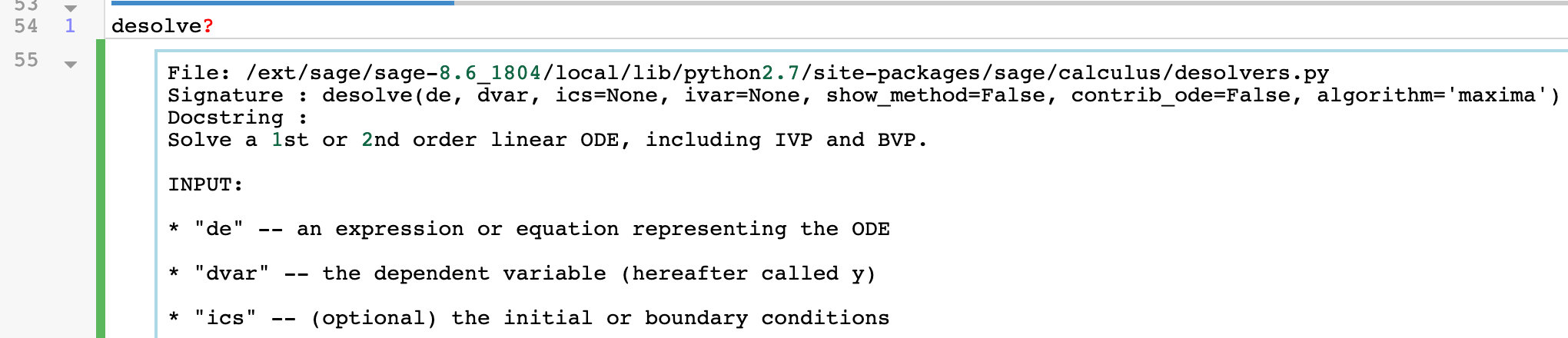
Source Code¶
To see source code for language features, append two question marks and run the cell.

Tab Completion¶
To get a hint for possible completions of a function name, method argument, etc., type the beginning of what you are looking for then press the [tab] key. This is a quick way to browse through the methods for an object.
Sage Worksheet Slow When Plotting? Disable svg.¶
Plots can generate a large number of points. The default display format for plots is svg , which gives excellent detail, but consumes an amount of memory proportional to the number of points and can markedly slow down worksheet performance.
You can efficiently display plots with as many points as you want if you use show() with an option of svg=False , for example:
show(plot(sin(x^2),(x,0,10)),svg=False) This approach also works with list_plot() . There's no way at present to default to svg disabled. You must use the setting with each plot.
How Long are Definitions Stored in a Sage Worksheet?¶
Definitions (of variables, functions, etc.) are stored in the worksheet process and are retained until that process terminates. The worksheet process may end by itself, for example when Restart is clicked at the top of the worksheet. It is also terminated when the sage worksheet server terminates or is restarted, when the project is stopped or restarted, and when the host virtual machine restarts.
Projects are stopped after some number of hours of non-interactive use (see Idle Timeout). If your project is on a free server, it will be stopped whenever the Google pre-emptible server instance restarts, typically once per 24 hours.
SageMath built-in functions save , load , save_session and load_session are useful for saving and restoring state. See Loading and saving sessions and listing all variables.
Wiki resources¶
Conversion utilities¶
- There are buttons in the UI to convert to PDF, a print-button or a Jupyter Notebook
- SageWS to HTML (including a utility to extract the sagews file from a generated HTML file)
- Run
cc-sagews2pdf --helpin a Linux Terminal for more information about converting to PDF - Similarly,
cc-sagews2ipynbis a command-line utility to convert Sage worksheet to Jupyter notebook, andcc-ipynb2sagewsdoes the reverse conversion, from Jupyter notebook to Sage worksheet.
Howto¶
How can I connect an HTML form with my Python code?¶
Note
The following explanation might be outdated!
To create a connection between your HTML form in a .sagews file created using HTML, CSS and JS, you need to use the worksheet.execute_code() function in your JS code.
Because worksheet.execute_code isn't a standard JS function, but special CoCalc function, you need to load your JS code with worksheet.execute_code() . In particular do NOT use
load('path/to/js/code.js') but instead use
salvus.javascript(open('path/to/js/code.js').read()) For example in a .sagews file suppose you created a div with id='myApp' as follows:
%html <div id='myApp'> .... <div id="msgLog"></div> <div id="msgErr"></div> </div> Let's say your Python function will double x :
def myfunc(x): print(x*2) In your JS code type:
worksheet.execute_code({ code: 'myfunc(n)', data: {n: 2}, preparse: true, cb: function(msg){ if(msg.stdout){$('#myApp #msgLog').html(msg.stdout);} if(msg.stderr){$('#myApp #msgErr').html(msg.stderr);} } }); Please note that myfunc() doesn't return anything. On the contrary, it uses print() to send output. This is because JS and python are different languages, and you can't just use return in your Python function to return some answer. stdout in JS code means standard output stream. That is, the print function in your Python code places the result of myfunc() in the output stream. That's why you need to use print() but not return() in your Python code.
Also, if your Python code will raise some exception, then it will result in output to stderr the standard error stream. If you JS code (as in the example above) catches stderr, you can get any error message from your Python code.
How can I play sounds?¶
CoCalc runs on a remote machine in the cloud. To make a wav, mp3 or ogg file play on your computer, it must travel from the cloud to your browser. That's done by first saving the waveform to a file in CoCalc and then downloading it into the website inside an HTML5 audio tag.
- Run the code below to render a waveform to a file using scipy.io.wavfile.write:
from scipy.io.wavfile import write as write_wav import numpy as np # Samples per second sps = 22050 # Frequency / pitch of the sine wave freq_hz = 440 # Duration per segment duration_s = 1.0 xx = np . arange ( duration_s * sps ) / sps yy = [] for i in range ( 5 ): yy . append ( np . sin ( 2 * np . pi * xx * freq_hz ) * np . cos ( 0.2 + ( i / 5.0 ) * np . pi * xx * ( 100 + freq_hz ))) yy = 0.3 * np . concatenate ( yy ) # 0.3 adjusts volume yy16bit = np . int16 ( yy * 32767 ) # Write the .wav file write_wav ( 'sound.wav' , sps , yy16bit ) -
Put this in a block of code. After evaluating it you'll see an embedded player:
%md <audio controls=true src="sound.wav"/>
Note
Currently, embedding into HTML5 via a %md Markdown cell does not work. Please check the status of ticket #4240.
Until it is resolved, run salvus.file('sound.wav') and click on the generated link to open the file in a new tab. Your browser should show you a little player.
Source: https://doc.cocalc.com/sagews.html
0 Response to "Simple Easy Basic Sagews Examples With Inputs"
Post a Comment